Clinical trials on medicinal products to be conducted in Sweden require approval from the Swedish Medical Products Agency. The applications to the Swedish Medical Products Agency provide an overview of the number of clinical trials on medicinal products that are planned in Sweden.
Number of applications received for clinical trials on medicinal products
The Swedish Medical Products Agency regularly presents statistics for the number of applications received (data from the journal “Information från Läkemedelsverket”, number 4 2015 and “Årsstatistik 2022 - kliniska läkemedelsprövningar”). When comparing EudraCT (European Union Drug Regulating Authorities Clinical Trials Database) and the Swedish Medical Product Agency’s case management system, the number of applications received differ slightly, but over time both sources show similar trends.
The differences are caused primarily by the Swedish Medical Product Agency’s case management system including resubmissions, and that VHP applications (voluntary harmonisation procedure, a process for joint EU evaluation of applications) are registered at different times with the national medical product agencies compared to the original registration in EudraCT.
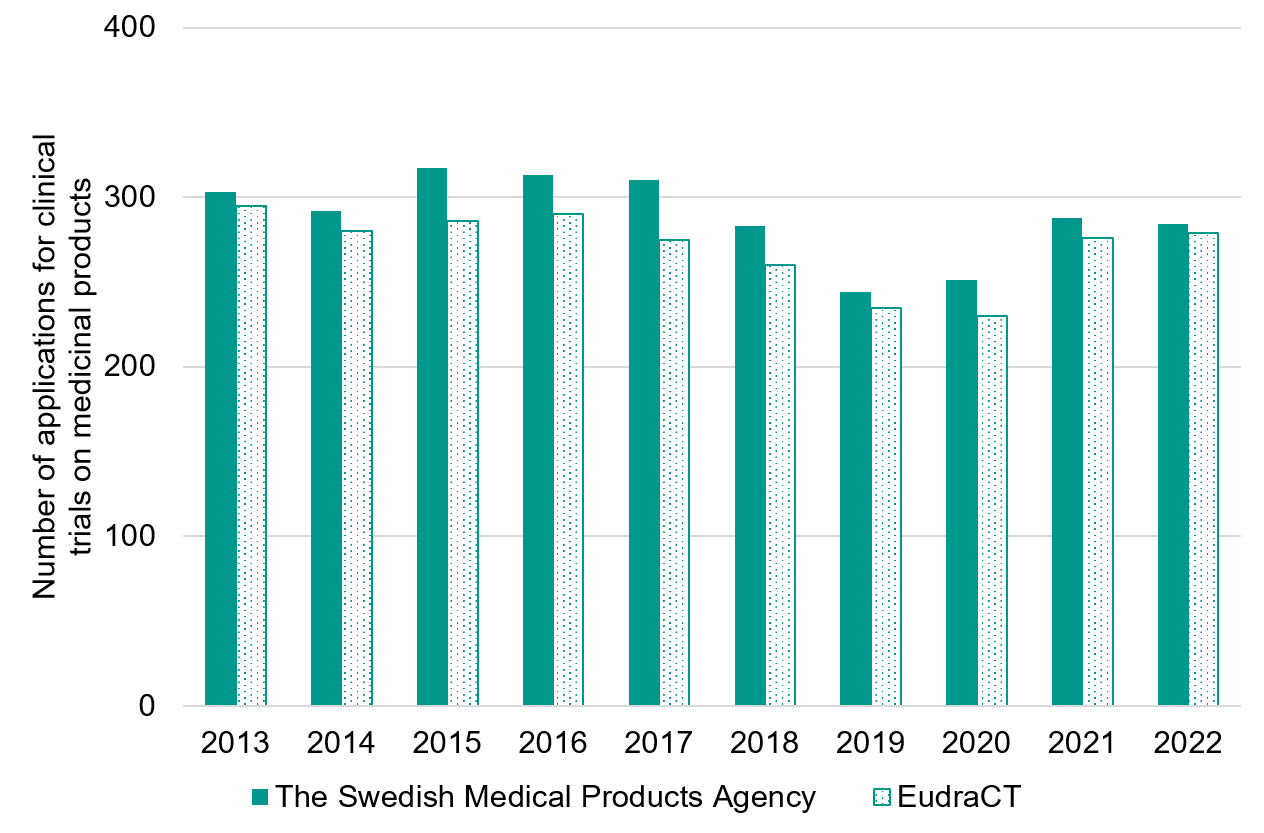
Figure 1. Number of applications received for clinical trials on medicinal products based on information from the Swedish Medical Products Agency’s annual statistics for clinical trials of medicinal products. For 2022, the Swedish Medical Products Agency also includes clinical trials on medicinal products managed via the Clinical Trials Information System (CTIS).
Year | The Swedish Medical Products Agency | EudraCT |
|---|---|---|
2013 | 303 | 295 |
2014 | 292 | 280 |
2015 | 317 | 286 |
2016 | 313 | 290 |
2017 | 310 | 275 |
2018 | 283 | 260 |
2019 | 244 | 235 |
2020 | 251 | 230 |
2021 | 288 | 276 |
2022 | 284 | 279 |
Applications divided up into commercial and academic clinical trials on medicinal products
The Swedish Medical Products Agency’s annual statistics show information on how the number of applications is divided up between academic and commercial clinical trials on medicinal products*. The number of clinical trials on medicinal products has been relatively stable during the last 10-year period, for both academic and commercial sponsors. A small reduction is noted for commercial trials during 2019–2020, followed by a recovery in 2021–2022. The proportion of commercial clinical trials on medicinal products is around 70% (average for 2020–2022).
* The concepts of “industry-sponsored” or “company-sponsored” are often used synonymously with “commercial” clinical trials on medicinal products. The concept of “non-commercial” is used correspondingly for “academic” clinical trials on medicinal products. The concepts are based on the regulatory division of the responsible sponsor of applications to the Swedish Medical Products Agency.
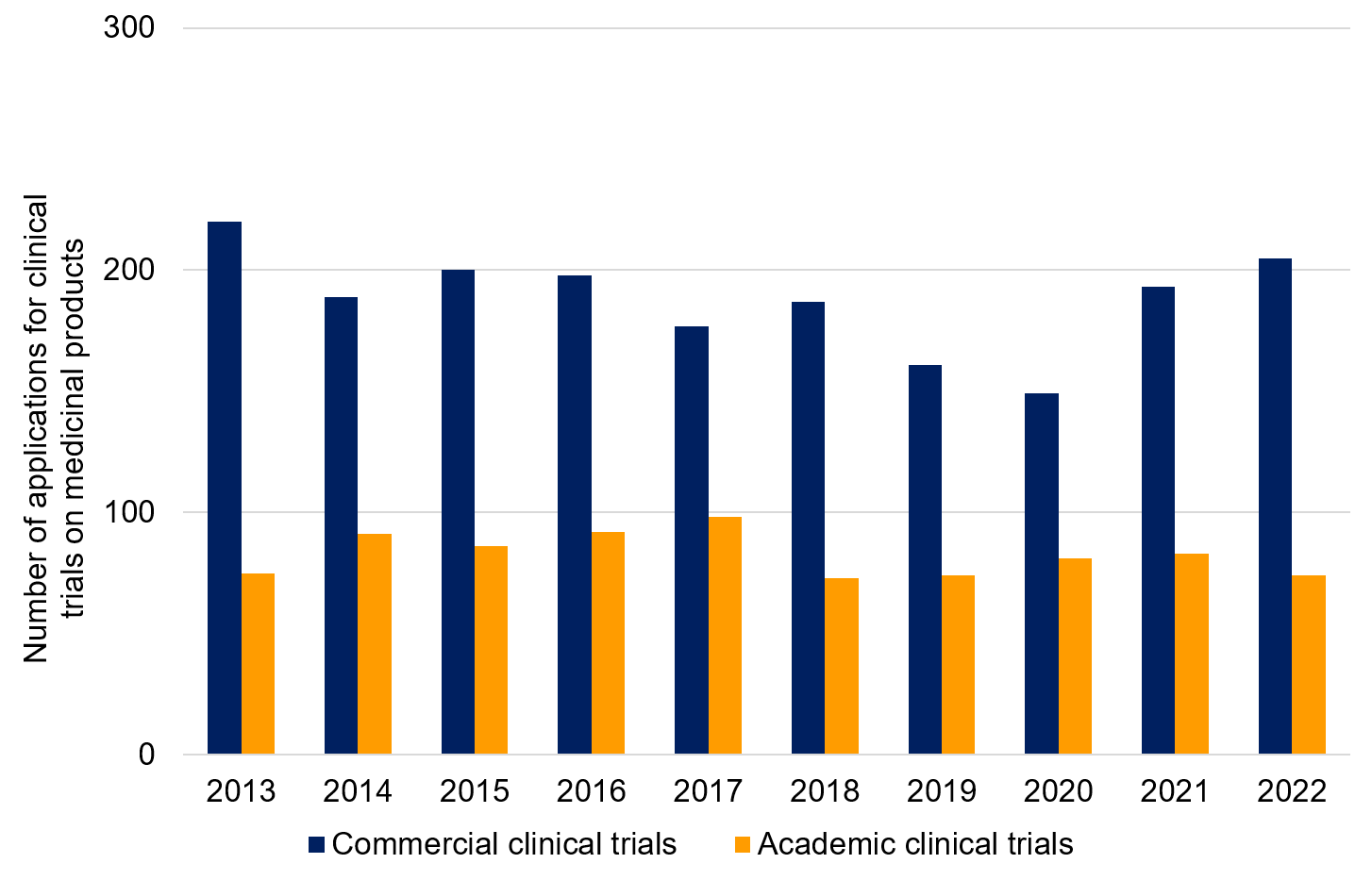
Figure 2. Number of applications received for clinical trials of medicinal products to EudraCT divided up per sponsor type: commercial or academic.
Year | EudraCT received | EudraCT received |
|---|---|---|
2013 | 220 | 75 |
2014 | 189 | 91 |
2015 | 200 | 86 |
2016 | 198 | 92 |
2017 | 177 | 98 |
2018 | 187 | 73 |
2019 | 161 | 74 |
2020 | 149 | 81 |
2021 | 193 | 83 |
2022 | 205 | 74 |
Clinical trials on medicinal products divided up per study phase
Annual statistics from the Swedish Medical Products Agency include information on how applications for clinical trials on medicinal products are divided up into different study phases (Phase I-IV)*. The distribution is 13% for Phase I, 31% for Phase II, 45% for Phase III and 11% for Phase IV (average for 2020–2022; studies lacking phase data have been excluded).
* Description of the different study phases in a clinical trial on medicinal products. Phase I focuses on safety and dosage, Phase II evaluates efficacy and safety on a larger scale, Phase III confirms the result in an even larger and more varied population ahead of agency approval, and Phase IV relates to after-market monitoring of the medicinal product’s effects when used by broader population groups.
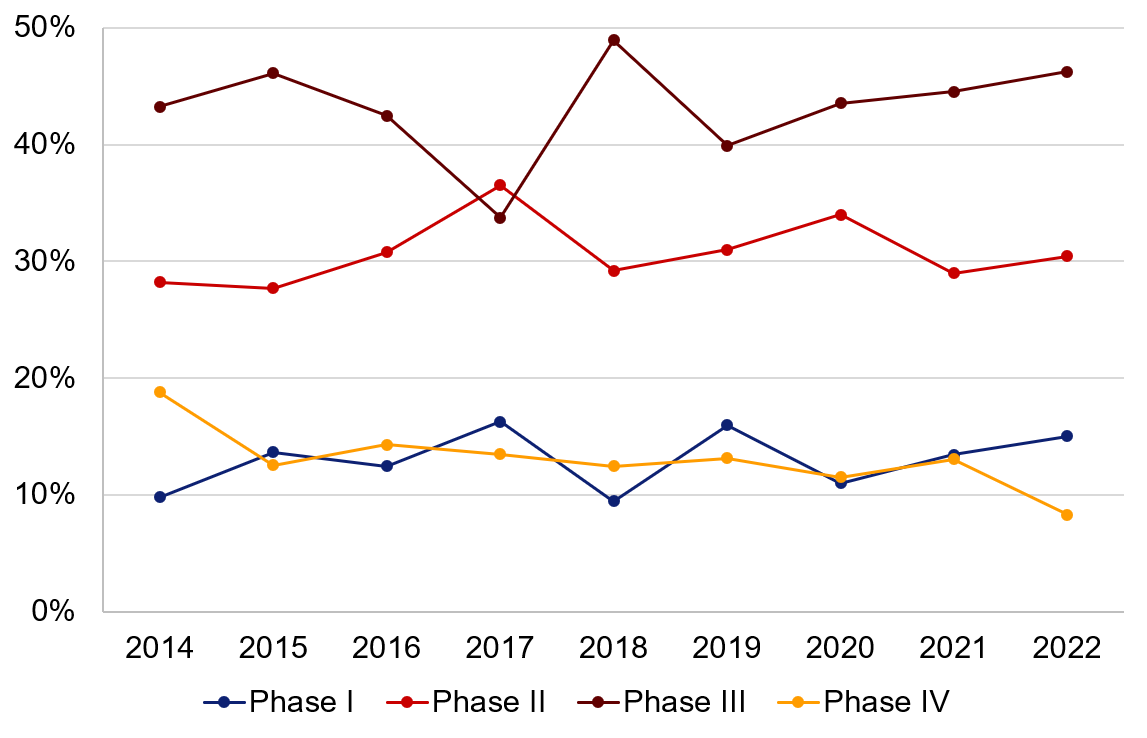
Figure 3. Number of applications received for clinical trials on medicinal products divided up into different study phases (studies lacking phase data have been excluded).
Phase I | Phase II | Phase III | Phase IV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
2014 | 10% | 28% | 43% | 19% |
2015 | 14% | 28% | 46% | 13% |
2016 | 12% | 31% | 42% | 14% |
2017 | 16% | 37% | 34% | 13% |
2018 | 9% | 29% | 49% | 12% |
2019 | 16% | 31% | 40% | 13% |
2020 | 11% | 34% | 44% | 11% |
2021 | 13% | 29% | 45% | 13% |
2022 | 15% | 30% | 46% | 8% |
Number of applications approved for clinical trials on medicinal products
An excerpt from the Swedish Medical Product Agency’s register (June 2023) shows that a large proportion of all applications are approved. In 2020–2022, 94 per cent of the applications were approved on average. The number of rejections was 1 per cent during the same period. This figure has been between 1 and 2 per cent in previous years as well (data from the Swedish Medical Products Agency’s journal “Information från Läkemedelsverket”, number 4, 2015). The number of applications received can therefore be assumed to be representative of the number of approved applications over time.
Approved | Rejected | Other | |
|---|---|---|---|
2020 | 206 | 2 | 10 |
2021 | 262 | 2 | 3 |
2022 | 238 | 6 | 21 |
The years are the year the case in question was received by the Swedish Medical Products Agency, even if the decision is sometimes made the following year. Decisions designated as “other” usually mean that the application was recalled or ran out of time, or that a decision has not yet been taken (for 2022, three cases were waiting for a decision in June 2023).
More information about clinical trials on medicinal products
The Swedish Research Council has previously published two reports with more detailed information and statistics for clinical trials on medicinal products based on excerpts from the Swedish Medical Products Agency with data from EudraCT for the years 2010–2018. The reports include the planned number of research subjects per study and variations over time, geographical distribution of trials across Sweden’s healthcare regions, age distribution and proportion of studies where children take part as research subjects, visualisation of the healthcare regions’ participation in multi-centre studies, and the distribution of number of studies and research subjects across different disease areas.
The reports also include several comparisons that show differences between academic and commercial clinical trials on medicinal products. For example, they show that academic clinical trials on medicinal products:
- are usually carried out in one healthcare region, while most commercial clinical trials on medicinal products have participating clinics in several regions and in other countries
- usually take longer before they are reported as completed and include considerably more research subjects per clinic.
Statistics for clinical trials on medicinal products (report in Swedish) External link.
External link.
PublISHED ON
UpDATED ON





