There are several different national and international data sources with information on clinical studies, but they often have a low or varied degree of coverage, and the information is not always kept updated. To get an idea of the number of planned clinical studies, you can look at applications to the Swedish Ethical Review Authority and the Swedish Medical Products Agency. On the other hand, there is no reliable source of information on when clinical studies begin and end, or what results they find.
Applications to the Swedish Ethical Review Authority provide an overview of the number of clinical studies planned
All clinical studies require ethical approval before they start. The number of new ethical review applications relating to medical research provides an indication of the number of clinical studies planned in Sweden. The Swedish Ethical Review Authority’s annual reports provide a good summary and show aggregated information on the total number of cases handled. However, these figures tell us nothing about the proportion of planned research that is actually started or concluded. To gain deeper understanding of the planned research and of individual studies, further information is needed.
Statistics on planned COVID-19 studies
Compiled data on ethical review applications
The Swedish Medical Products Agency and EudraCT/CTIS have information on clinical trials on medicinal products
Up until 2022/2023, all* clinical trials on medicinal products for human medicinal products approved by the Swedish Medical Products Agency were registered in EudraCT (European Union Clinical Trials Register) with the European Medicines Agency (EMA). As from January 2023, all new registrations are instead made in a new database called the Clinical Trials Information System (CTIS). Having information on clinical trials on medicinal products accessible to the general public is a requirement of the EU Regulation No (EU) 536/2014. EudraCT has searchable information on about 4 250 clinical trials on medicinal products carried out in Sweden from 2004 and onwards (according to a search in June 2023). Investigators and sponsors are responsible for keeping the study status updated, and for reporting results from the trials.
Statistics for clinical trials on medicinal products
CTIS - European Medicines Agency (EMA) External link.
External link.
EudraCT - European Medicines Agency (EMA) External link.
External link.
* Some information relating to Phase I studies is not published openly. Phase I studies where only adult research subjects are included, or that are not part of a paediatric investigation plan (PIP) are not published either.
International data sources with information on all types of clinical studies
There are many different international databases with information on clinical studies. The databases aim to make information on clinical studies accessible and are also used to make international comparisons.
For Swedish clinical studies, the most common one is ClinicalTrials.gov for study registration, although registration is voluntary and far from all clinical studies are registered. The greatest number of clinical studies are found in the WHO’s database ICTRP, as this gathers together studies from ClinicalTrials.gov, EudraCT (now CTIS) and several other sources. In general, the degree of coverage of clinical studies in the databases is low compared with the number of ethical approvals.
ClinicalTrials.gov
ClinicalTrials.gov is an American database whose original focus was on registering clinical trials on medicinal products carried out in USA. Nowdays it is the most used database for researchers and companies around the world who wish to register ongoing clinical trials on medicinal products or other clinical studies. Excerpts from the database are often used in reports, scientific publications, and international comparisons. For example, the database was used early on during the COVID-19 pandemic to analyse and monitor the research that was starting around the world (information from the on-line journals BMJ Open, article 2020; 10:e041276 and JAMA Intern Med, article 2020; 180(10):1398-1400).
In total, ClinicalTrials.gov covers information on around 8 000 clinical studies in Sweden, of which 1 900 are ongoing*. Every year, 400–500 new Swedish clincal studies are registered in the database. Based on data from the Swedish Ethical Review Authority, it can be estimated that the degree of coverage in ClinicalTrials.gov amounts to around 21 per cent of the clinical studies with ethical approval**. During 2020–2022, around 65 per cent of the clinical trials on medicinal products were registered, compared with the number of approved applications from the Swedish Medical Products Agency (which represents around 460 clinical trials on medicinal products registered in ClinicalTrials.gov, and around 710 applications approved by the Swedish Medical Products Agency.
The proportion of clinical trials on medicinal products and other clinical studies registered in ClinicalTrials.gov varies between countries, as registration is often voluntary and as there are many alternative national databases (these are listed on the page “Primary registries in the WHO registry network” on the WHO’s website). There is also great variation regionally within Sweden in relation to study registration in the database, as the regions have differing requirements in relation to registration***. For the studies registrered, there is a balance in favour of clinical trials on medicinal products, although the number of other studies has increased over time on the part of Sweden.
ClinicalTrials.gov database (U.S National Library of Medicine) External link.
External link.
* A search (in ClinicalTrials.gov) on Sweden and studies with the status “Recruiting”, “Active, not recruiting” and “Enrolling by invitation” produced 1 923 hits in July 2023.
** As from 2008 and onwards, there are annual reports with information on the number of medical applications received. It is estimated that around 33 000 ethical review applications during the period 2008–2022 were approved, at the same time as around 6 800 studies were registered in ClinicalTrials.gov.
*** Karolinska Institutet (through its employee portal) encourages researchers to register studies in ClinicalTrials.gov. Corresponding encouragements are lacking from most other regions.
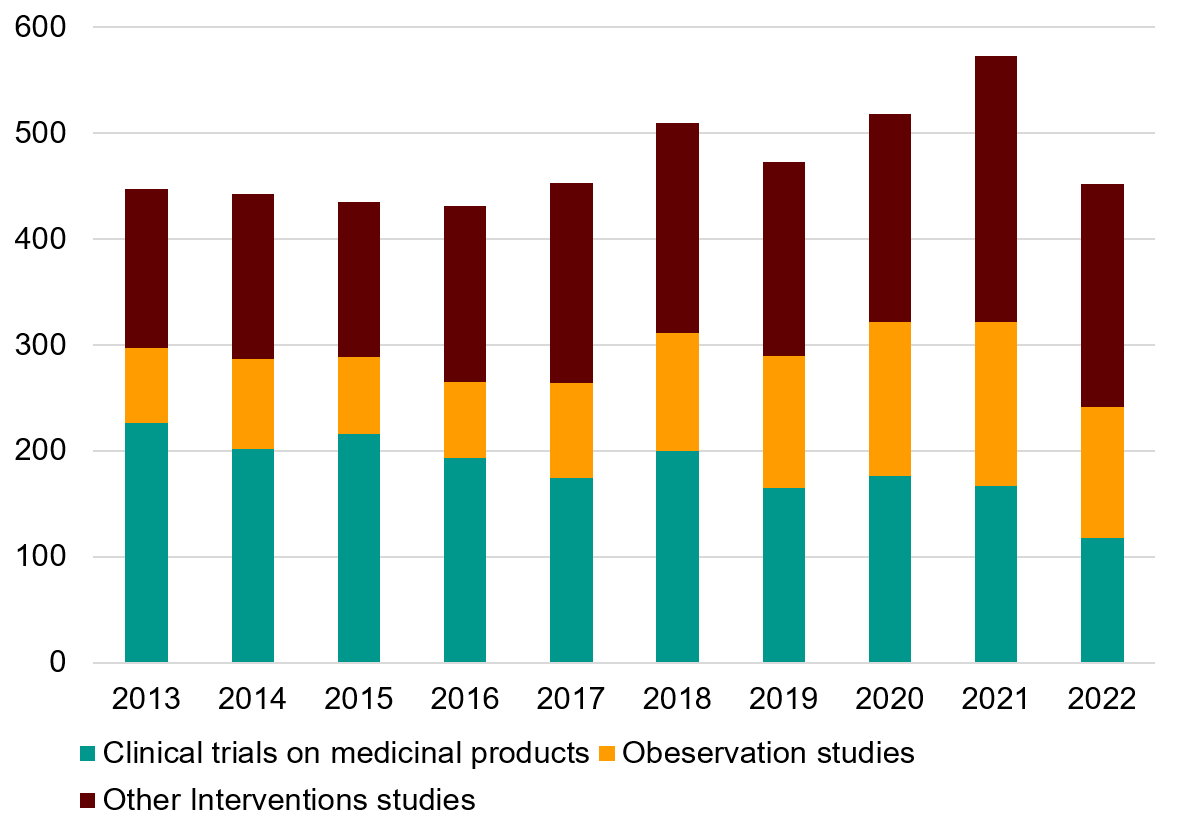
Figure 1. Development of the number of Swedish studies registered in ClinicalTrials.gov. The years are based on the variable “First posted”, which corresponds to the date when the information became accessible in the database.
Facts to consider when analysing using data from ClinicalTrials.gov
- The focus is on clinical trials on medicinal products although not all are registered. Other types of clinical studies are also registered, but it is unclear at what coverage rate.
- Registration is often voluntary, although there might be compelling incentives in some countries*. In international comparisons, you can supplement information from the WHO’s database ICTRP to get as complete a picture as possible**.
- Use of ClinicalTrials.gov to register clinical studies varies over time. Internationally, it has declined in favour of other, often national, databases***, which makes it difficult to discover trends in numbers of studies using this source.
- Study registration often occurs after a delay in relation to when a study is approved by the Swedish Ethical Review Authority or the Swedish Medical Products Agency.
- Low degree of coverage in relation to the number of approved ethical review applications. Difficult to compare the degree of coverage between different countries, as the ethical review process differs and is often considerably more decentralised than in Sweden.
* Information from the on-line journal BMJ Open, article 2018; 361:k1452.
** Information from the National Library of Medicine/Journal of the Medical Library Association, article 2014; 102(3):177–83.
*** Information from the on-line journal Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, JCE, article 2019; 116:106–113.
ICTRP
The WHO’s database ICTRP (International Clinical Trials Registry) has information on almost 14 000 ongoing and concluded studies, where Swedish research subjects have participated since 2004/2005. It is not possible to register study information direct in ICTRP; instead, the database collects information from several different international and national databases. The underlying databases often have a larger amount of information on each study than is presented in ICTRP.
For Swedish clinical studies, ICTRP collects data primarly from ClinicalTrials.gov: 56 per cent, EudraCT: 32 per cent, and ISRCTN: 4 per cent (the percentage corresponds to the proportion of studies from each database stating that research subjects from Sweden are taking part, June 2023). The remaining clinical studies are collected from different national databases of varying sizes, such as the German Clinical Trials Register and the Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry. The WHO is responsible for screening out the double registrations that may arise as a result of data being collected from different sources (further information is available on the page “Unambiguous trial identification” on the WHO’s website.
ICTRP database (WHO) External link.
External link.
Facts to consider when analysing using data from ICTRP
- ICTRP is the database where you can find the greatest number of Swedish clinical studies, and this is probably the case for most other countries too, as ICTRP includes several major national databases.
- To capture as many clinical trials as possible, ICTRP can be used as a complement* to ClinicalTrials.gov when you want to make different types of comparisons or analyse the development of a certain scientific field.
- The amount of information in the underlying databases varies, which means that some study information is not always complete, or possible to compile in a uniform way.
* Information from the on-line journal Nature Research Journals, npj Regenerative Medicine, article (2019) 4:20.
ISRCTN Registry
All types of clinical studies can be registered in the ISRCTN Registry. The database is linked to open publication of scientific publications, and can be seen as a European alternative to ClinicalTrials.gov, but it includes considerably fewer registered clinical studies. Around 40 Swedish clinical studies are registered in ISRCTN per year (average for 2018–2022), and in total there is information on around 700 Swedish clinical studies (relates to studies that have a Swedish sponsor or recruitment of research subjects in Sweden, June 2023). As this only corresponds to around 2 per cent of the number of ethical approvals, it is not possible to make any deeper analysis based on documentation from the database.
ISRCTN Registry database (BioMed Central, part of Springer Nature) External link.
External link.
Open Swedish databases and regional follow-up
In addition to the international databases, there are several different initiatives at regional and national level. Some databases have the primary purpose of facilitating patient recruitment by showing the clinical studies that are open for inclusion. Other databases aim to follow up the clinical studies that are carried out at regional level.
Healthcare Region Mid Sweden
Forum Middle Sweden, a node in the Clinical Studies Sweden collaboration, systematically follows up ongoing clinical studies in the healthcare region Mid Sweden and publishes annual reports with summarising statistics. The follow-up is made possible by a well-established organisation with persons linked to research in the seven constituent regions. Nowdays there is also a searchable database where information on ongoing clinical studies is accessible. A search in June 2023 showed that there are almost 1 600 ongoing clinical studies (2 600 if studies at the planning stage are included). The studies can also be searched on Researchweb. Every year, 400 new clinical studies are started, which can be compared with the healthcare region having on average 360 ethical approvals for each of the years 2020–2022 (the figure can be expected to be higher, as information on the applications where regions in Mid-Sweden take part as participating research principals is lacking).
About clinical studies in healthcare region Mid Sweden 2022
- Academically initiated studies represent 86 per cent, and commercial clinical studies 14 per cent.
- The study types can be divided up into 48 per cent intervention studies, 39 per cent observation studies. The rest are classed as “other studies”.
- Cancer, followed by circulatory organ disease, are the most common diagnosis areas in terms of number of studies.
- The number of reported clinical trials on medicinal products have remained stable at around 340 per year during the last five years.
Karolinska University Hospital
During the last few years, the Karolinska University Hospital has developed a database for clinical studies. The public part of the database, which was launched in 2022, has information on around 400 clinical studies that are open for recruitment (according to a search in June 2023). Karolinska Institutet also encourages researchers to register their clinical studies in ClinicalTrials.gov*. There are around 1 100 ongoing clinical studies registered in the Stockholm region, of which just under 300 new clinical studies are registered each year. This can be compared with around 650 new ethial approvals each year with research principals from the Stockholm healthcare region (average for 2020–2022).
Karolinska University Hospital database for on-going clinical studies (in Swedish) External link.
External link.
* A search for Stockholm with the status “Recruiting”, “Active, not recruiting” and “Enrolling by invitation” produced 1 098 hits in July 2023.
Information on ongoing clinical studies in other regions
In other regions, the work on following up clinical studies varies. The Western Götaland and Halland regions have project databases in the Researchweb CRIS system and are searchable under the name of “FoU i Sverige”. In the open parts of the database, it is difficult to sort out clinical studies based on year, and in the Western Götaland region student projects are also registered, which makes it more difficult to make estimates of the degree of coverage in the database as compared to the number of ethical review applications. There are also other examples where there is good internal monitoring locally of ongoing clinical trials of medicinal products for example, or where some follow-up of clinical studies has begun. In general, it is currently not always possible to find lists of ongoing clinical studies in most regions, which in practice means that we are reduced to searching various international databases. Within the framework for Clinical Studies Sweden’s operation, a project team will in future be working more actively with follow-up of clinical studies, and to begin with the focus will be on clinical trials on medicinal products.
Researcweb database, FoU i Sverige (Minso Solutions, in Swedish) External link.
External link.
Clinical Studies Sweden website External link.
External link.
Cancer studies in Sweden
Cancer studies in Sweden is a database with ongoing cancer studies. Registration is voluntary, and around 300 ongoing clinical studies are registered in the database (according to a search in June 2023). The aim is to facilitate recruitment of study participants, and to strengthen and support Swedish clinical cancer research. It is difficult to assess the degree of coverage in the database. In comparison, there are 430 ongoing cancer studies in the healthcare region Mid Sweden (according to a search in June 2023), and ClinicalTrials.gov* has almost 600 ongoing cancer studies registered. It therefore seems as though many clinical studies are missing from Cancer studies in Sweden, and that voluntary registration is not sufficient as an incentive if it is to be possible to trace all clinical studies in the cancer field.
Cancer studies in Sweden (in Swedish) External link.
External link.
* A search for “cancer” for studies with the status “Recruiting”, “Active, not recruiting” and “Enrolling by invitation” produced 585 hits in May 2023.
Finding Clinical Studies (HiKS)
The industry organisation Lif is responsible for the newly started database HiKS, with information on around 160 ongoing industry-sponsored clinical trials on medicinal products across Sweden (of which around 70 are open for recruitment). The databasen can be seen as a constituent part of the clinical trials on medicinal products that are registered in ClinicalTrials.gov, but with information in Swedish. The figures can also be compared with the fact that, according to EudraCT, around 1 000 industry-sponsored clinical trials on medicinal products are ongoing in Sweden.
HiKS database (industery organisationen Lif, in Swedish) External link.
External link.
* A search for clinical trials on medicinal products with the status “Ongoing” in ClinicalTrialsRegistry, June 2023.
PublISHED ON
UpDATED ON



